Check tour
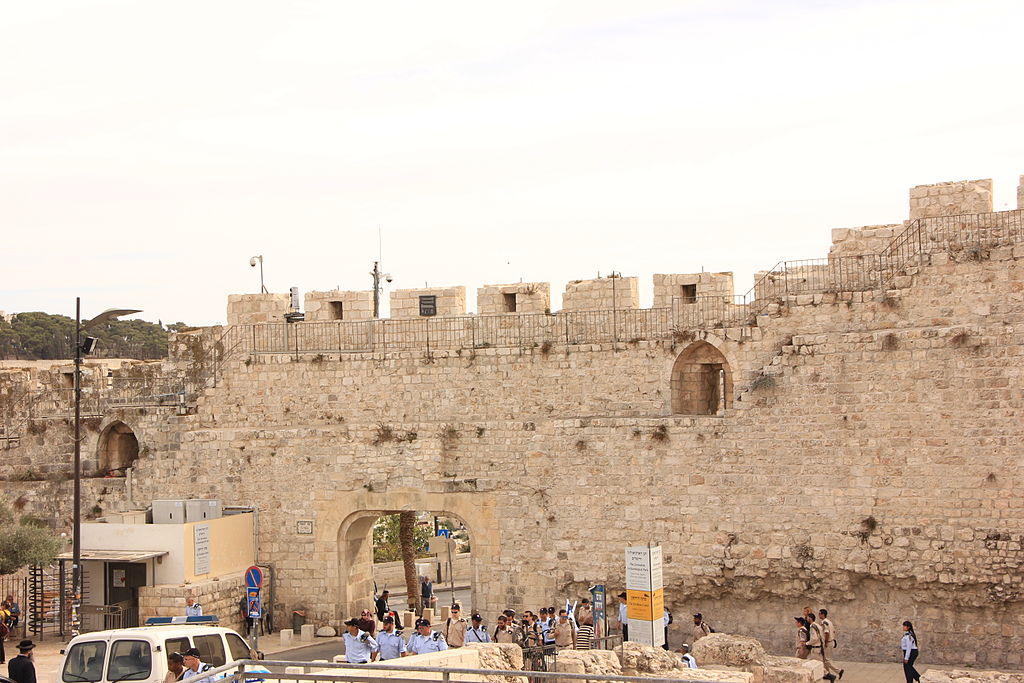
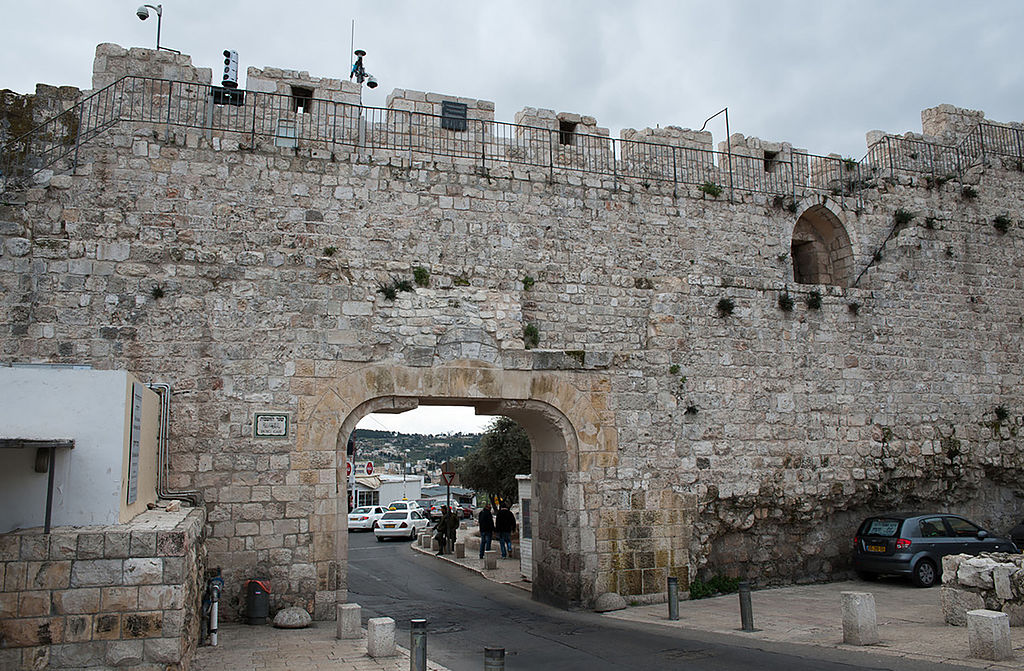
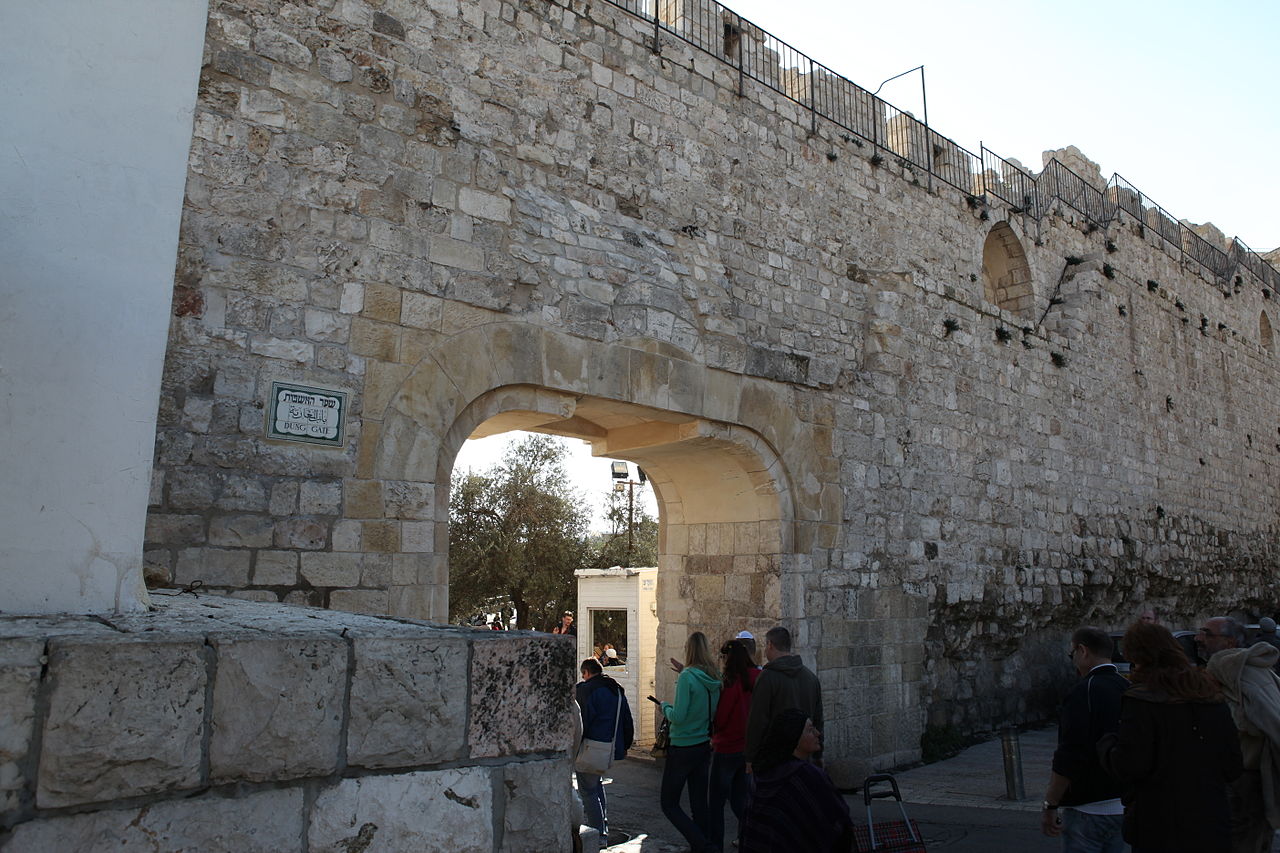
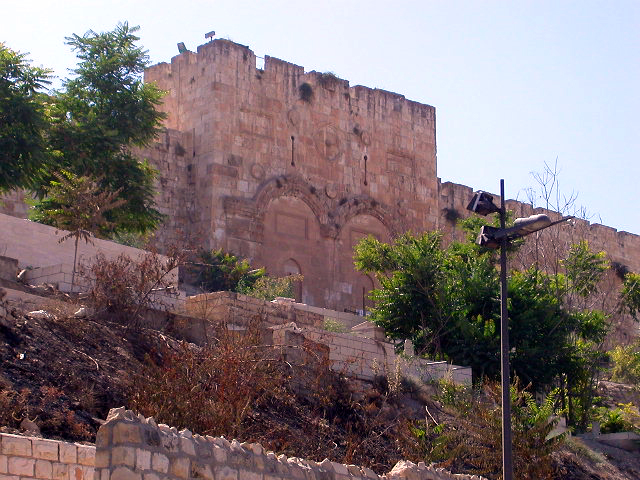
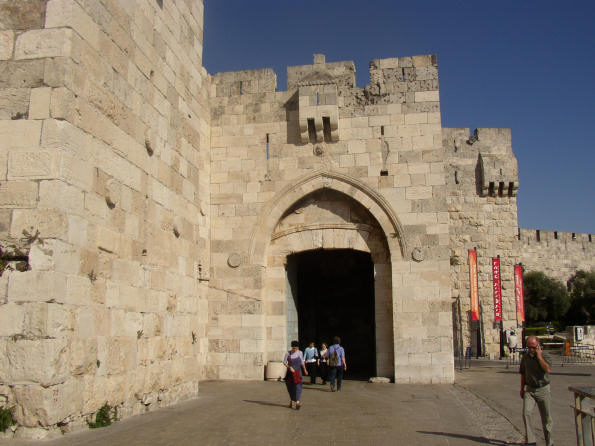
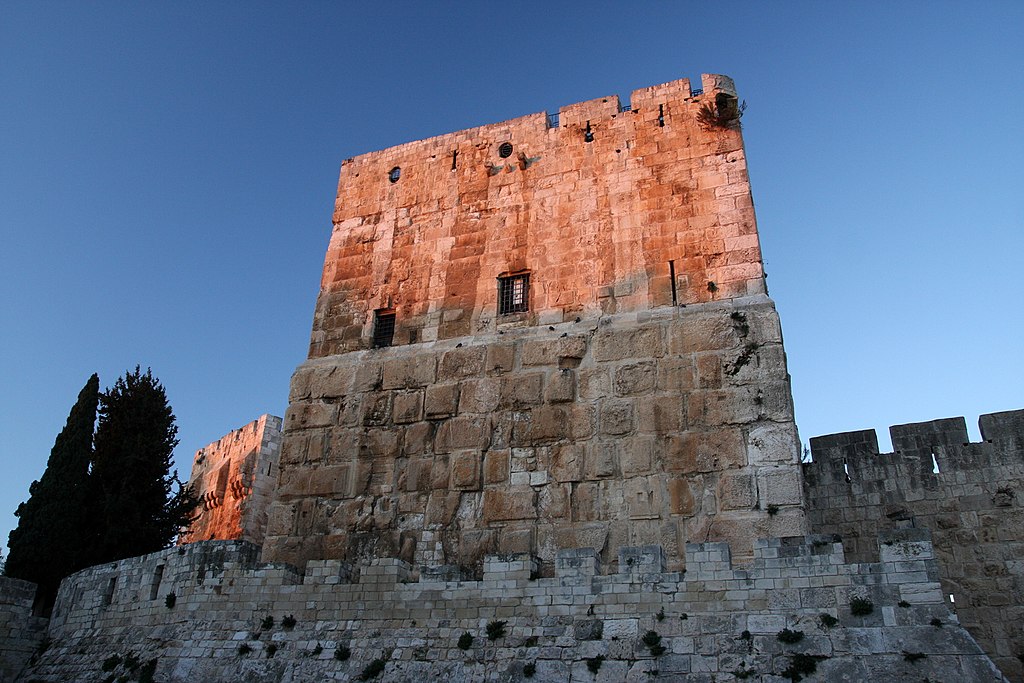
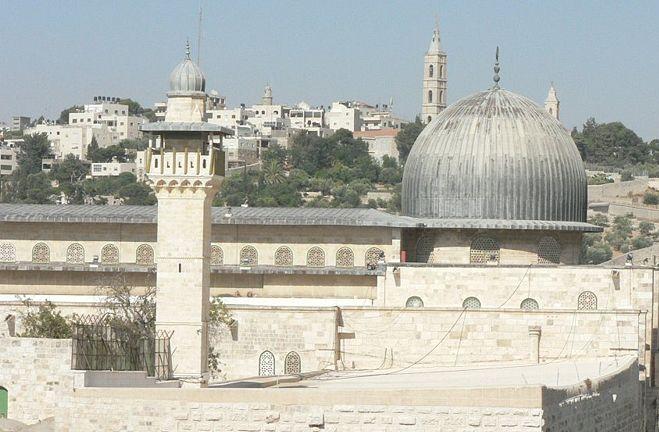
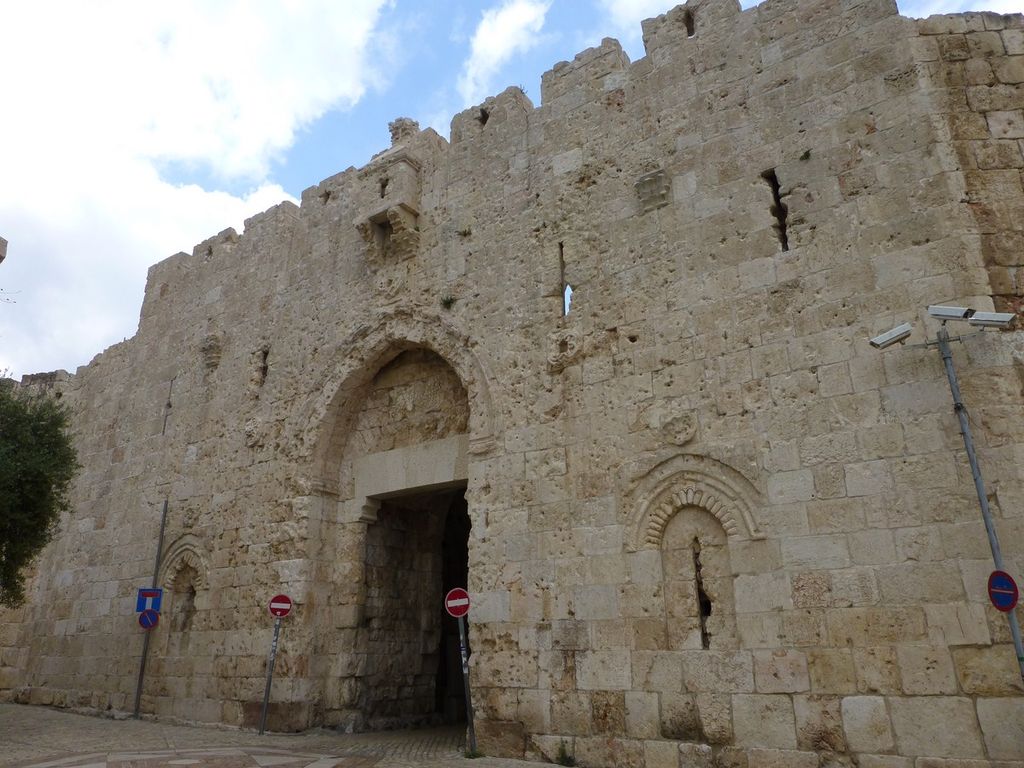
Dung Gate
Country Days Tracker - this app track the days you spend in different countries helping you with visas and tax residency. Try it now! Watch video!
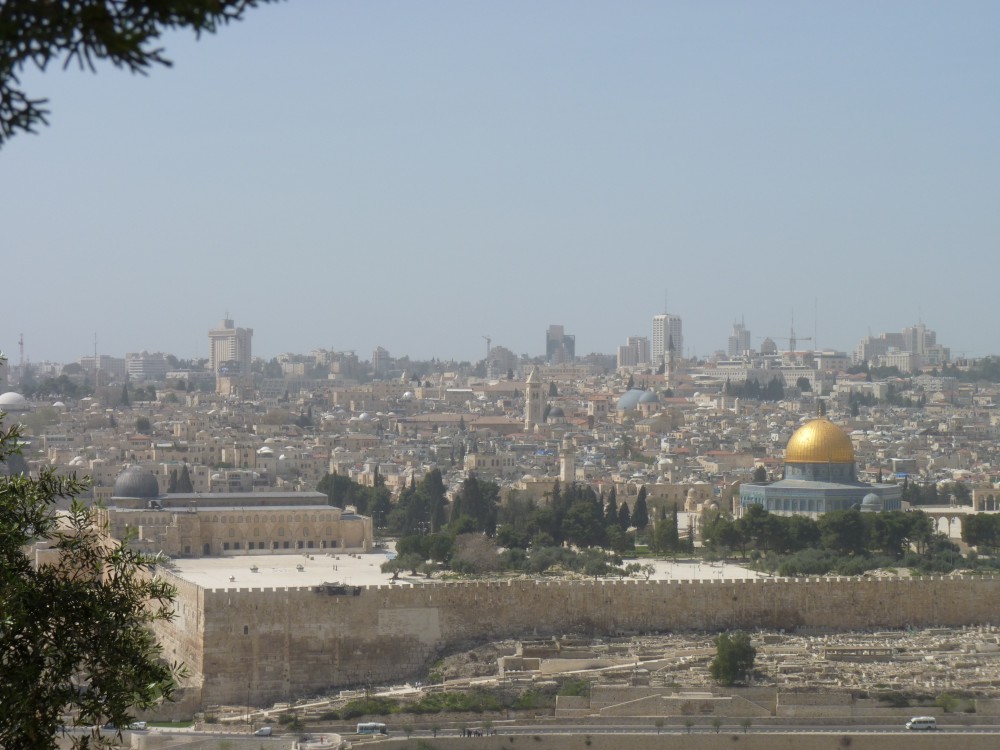
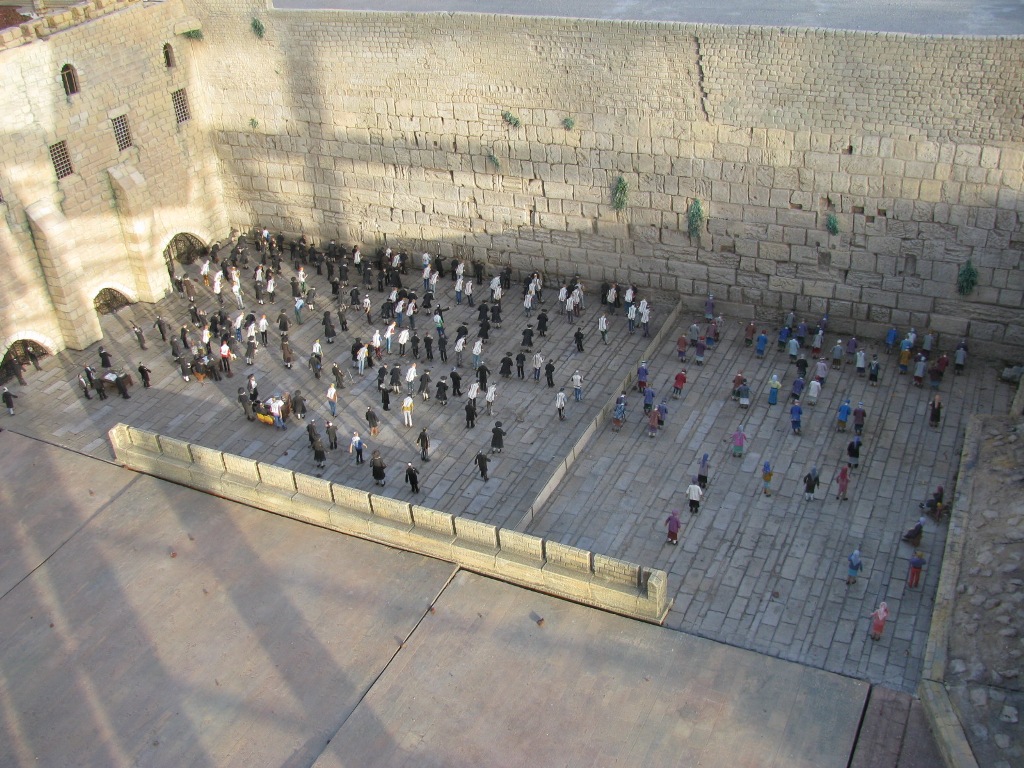
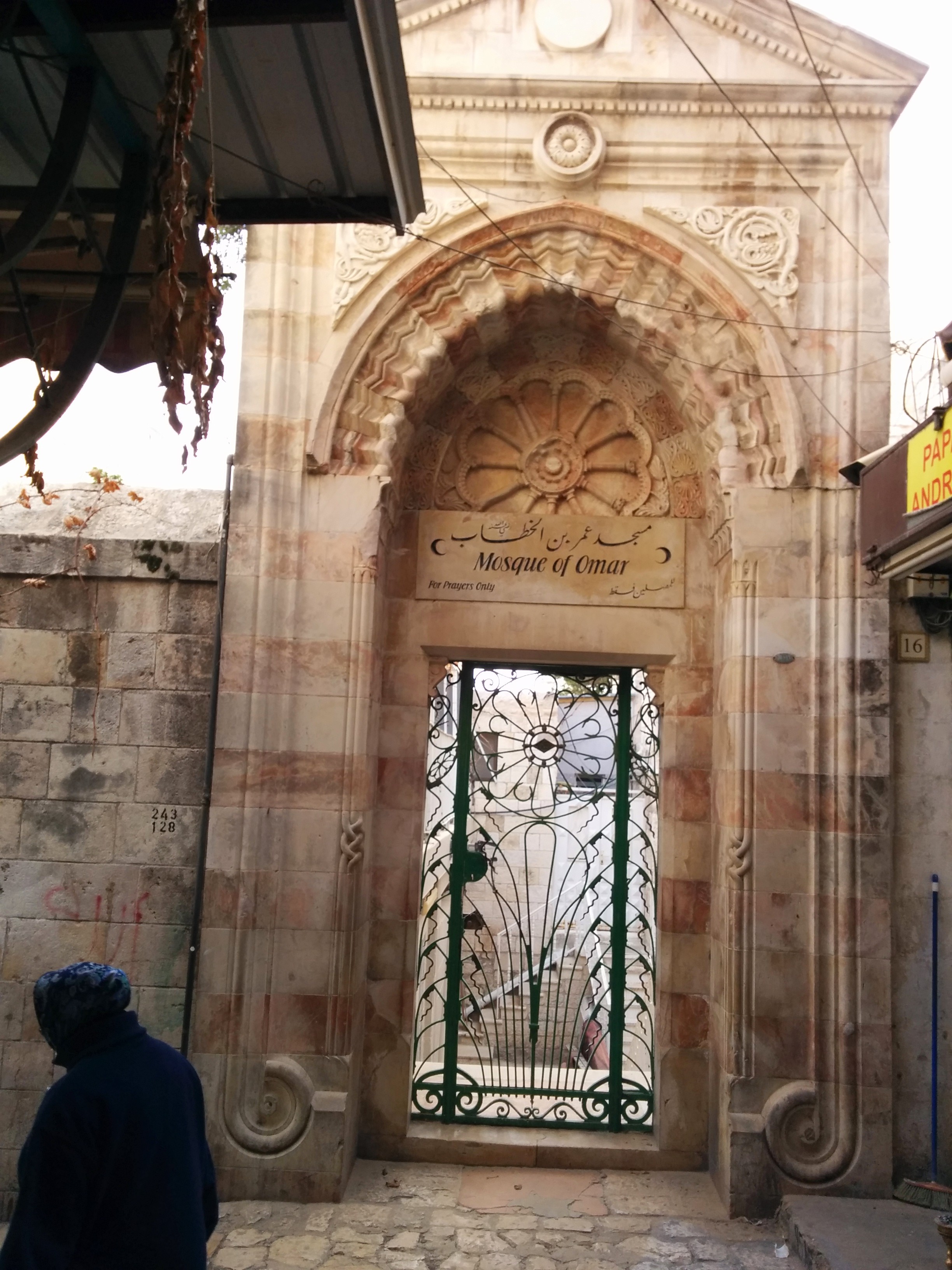
The Dung Gate, also known as Sha'ar Ha'ashpot in Hebrew, is one of the gates leading into the Old City of Jerusalem, Israel. It is located on the southern wall and provides access to the Jewish and Armenian Quarters.
History:
The Dung Gate has a rich historical significance. It is believed to be one of the oldest gates of Jerusalem, dating back to the time of the Second Temple period, around the 6th century BCE. During the time of Jesus, this gate was used as an exit for the disposal of rubbish and waste from the city, which is how it got its name. It was also the gate through which the Red Heifer was led outside the city for ritual burning.
Tips for tourists:
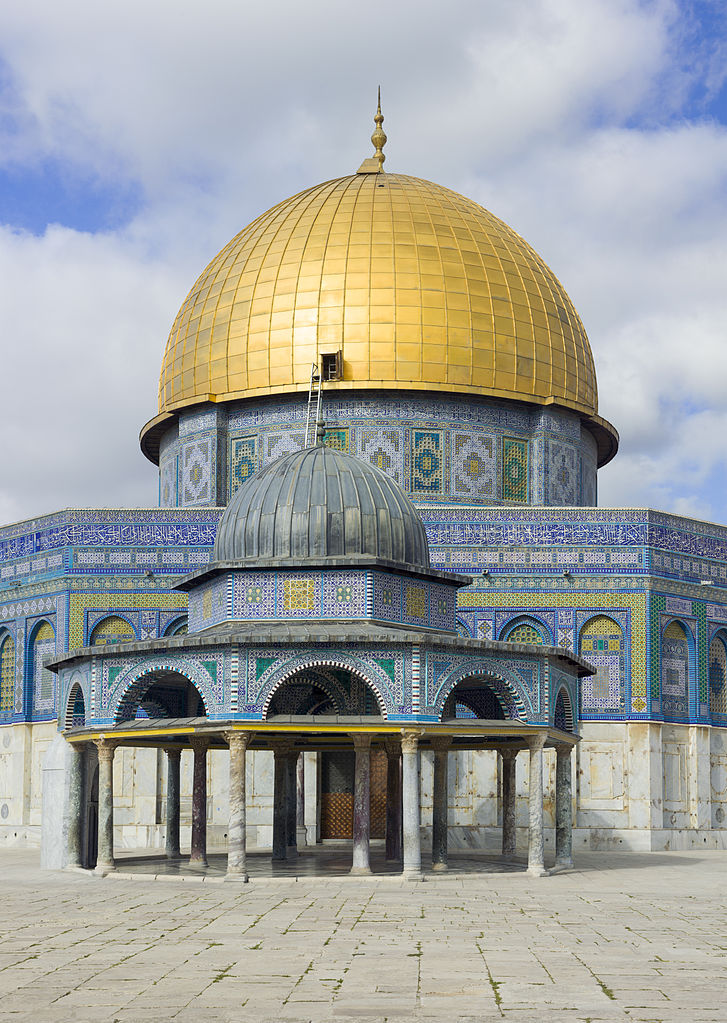
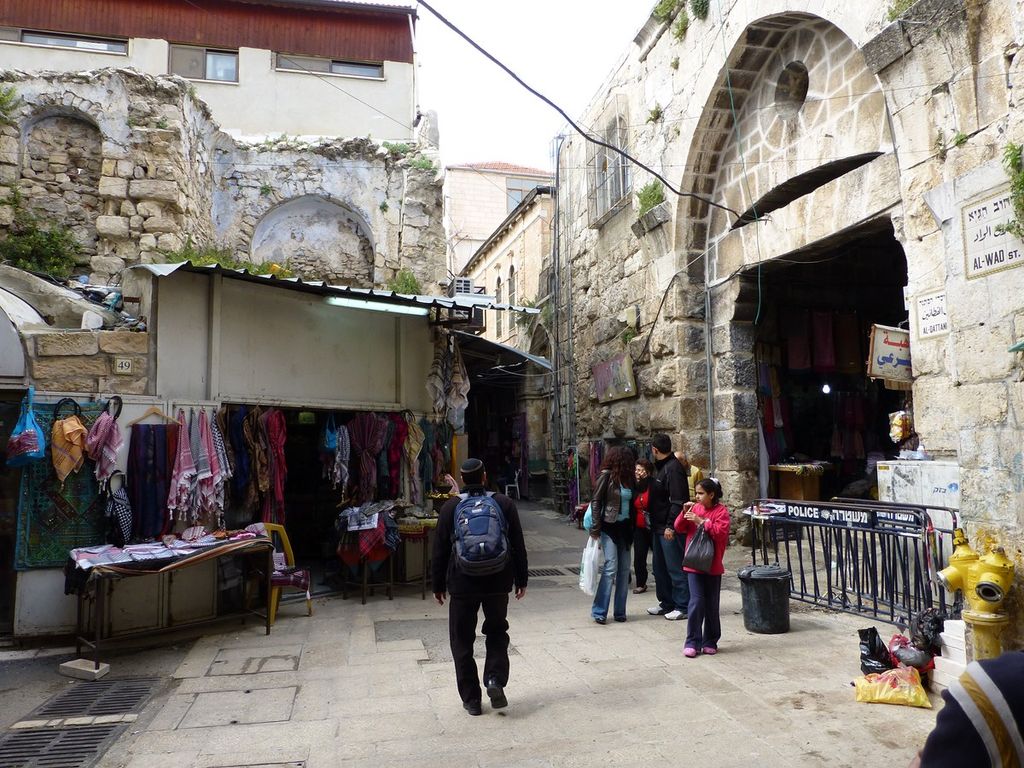
1. Access to the Temple Mount: The Dung Gate is the closest entrance to the Western Wall and the Temple Mount. Visitors who wish to access these sites often use this gate as it provides a convenient entry point.
2. Archaeological Park: Near the Dung Gate, there is an archaeological park known as the Ophel City Walls Excavations. It showcases remains of ancient structures and fortifications, offering visitors a glimpse into Jerusalem's rich history.
3. Security checks: Like other entrances to the Old City, the Dung Gate has security checks. Be prepared to go through metal detectors and bag inspections, especially during peak tourist seasons.
4. Dress modestly: As the Dung Gate provides access to religious sites, it is advisable to dress modestly, covering your shoulders and knees, out of respect for the local customs and traditions.
5. Explore the surrounding area: The Dung Gate is located near several other significant sites, such as the City of David, Mount Zion, and the Kidron Valley. Consider exploring these areas to enhance your visit to Jerusalem.
Visiting the Dung Gate allows tourists to experience the historical and religious significance of Jerusalem. It is an important entry point for accessing the Western Wall and the Temple Mount, making it a must-visit location for anyone exploring the Old City.